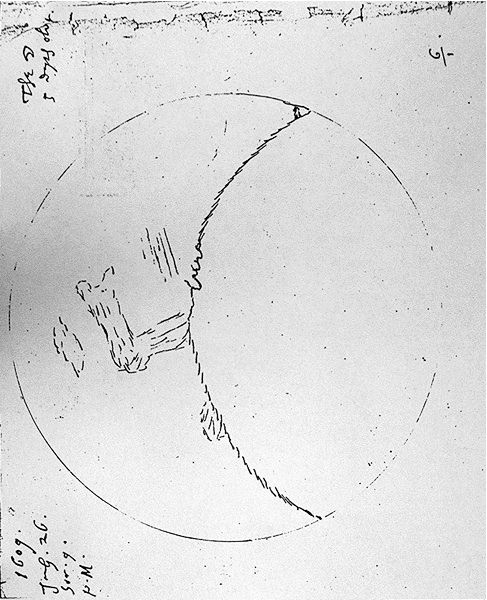
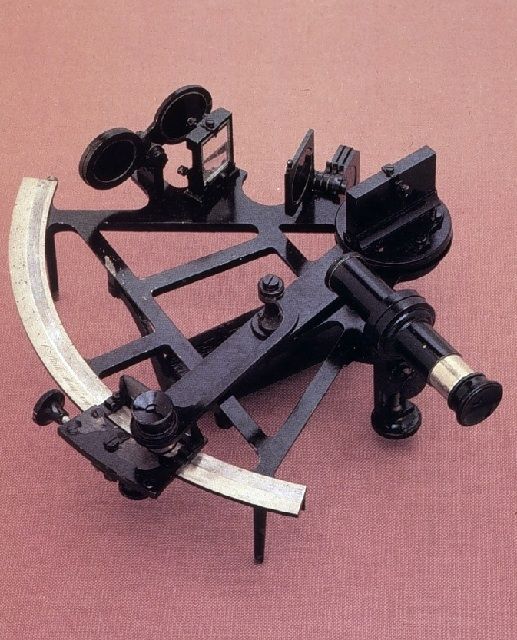
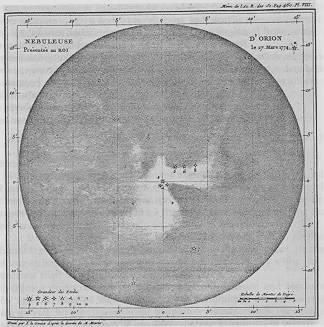
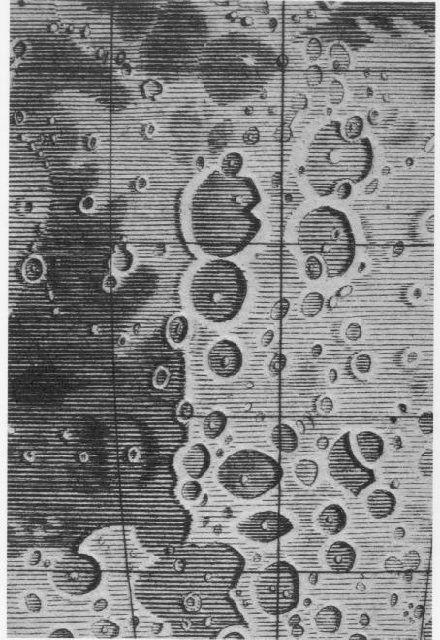
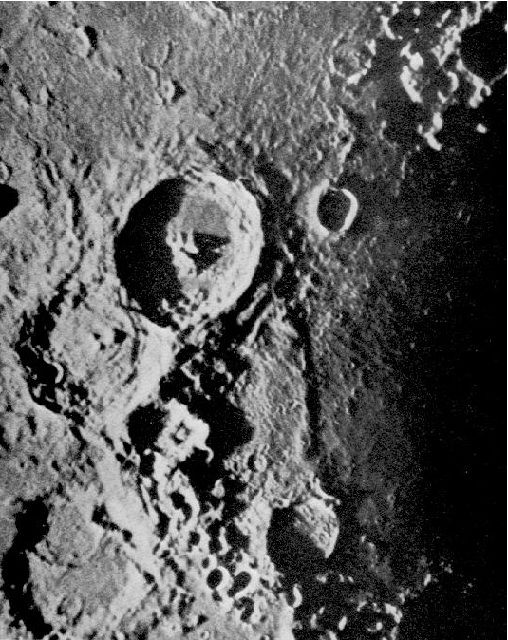
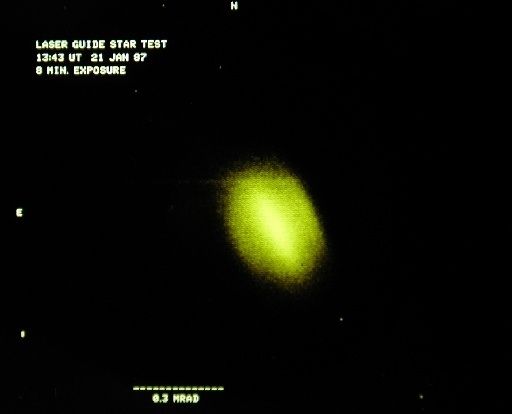
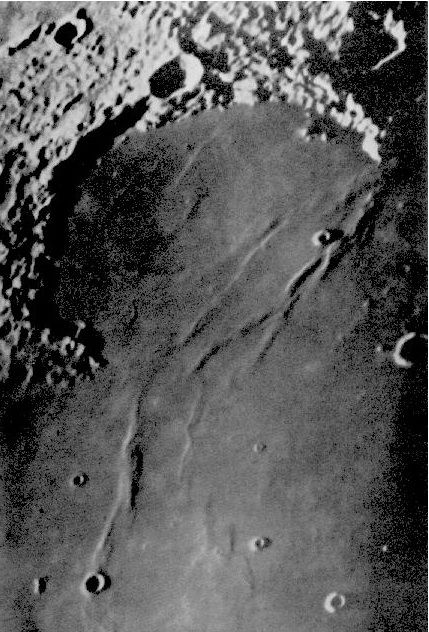
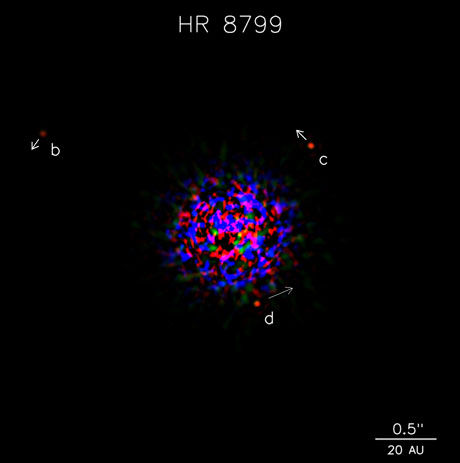
A Journey Into Astronomy
Before 1400
The astrolab and octant are the predecessors of the sextant.
Instruments
Before 1400
For thousands of years, native people use the stars to navigate and to monitor the passage of time. Stars are also the inspiration for native legends, which are passed down from generation to generation.
Observatories
Before 1400
The Assyrians are likely the first to use lenses to magnify objects, probably around 1,500 BC.
Instruments
1497
By exploring Newfoundland, John Cabot becomes the first known European to set foot on Canadian soil. Like all explorers of his time, he navigates using the stars.
Observatories
1535
Jacques Cartier explores the continental interior. He finds the mouth of the Saint-Lawrence during the Perseid meteor shower.
Observatories
1540
Leonard Digges constructs the first telescope using lenses.
Instruments
1618
Jesuits record the first astronomical observations made in Canada.
Observatories
1634
Astronomy becomes an official task assigned to the Engineer-in-Chief and Land Surveyor for the New France colony in Quebec.
Observatories
1646
Jean Bourdon is the first Canadian to own a telescope.
Observatories
1667
Louis XIV commands all roads in the capital of Paris to be lit at night in order to combat thefts and other crimes.
Astronomers
1669
Rasmus Bartholin publishes the first article on the splitting of light rays by Icelandic spar.
Instruments
1672
In France, Laurent Cassegrain invents a new type of reflecting telescope.
Instruments
1751
An engraving showing the image of sky observers outdoors with an astronomical instrument at the Fortress of Louisbourg in Nova Scotia. It is likely that a temporary observatory existed for a short time in the fortress.
Observatories
1792
William Murdoch invents the natural gas lamp and cities in Britain begin to light their streets using natural gas.
Astronomers
1816
Joseph Nicéphore Niépce succeeds in making the first photograph on paper.
Instruments
1836
British astronomer John Frederick William Herschel invents the photometer.
Instruments
1846
Dr. Charles Smallwood establishes an observatory at Saint-Martin on Quebec’s Île Jésus (now “Laval”).
Observatories
1849
Dr. James Toldervy of Fredericton, New Brunswick, creates an observatory in his garden near the Saint John River.
Observatories
1850
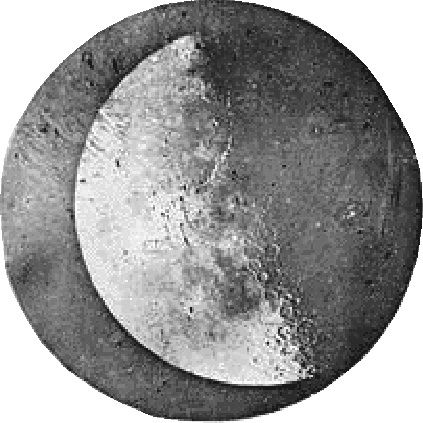
American astronomer William Cranch Bond and photographer John Adams Whipple produce the first photograph of a star when they take this daguerreotype of Vega.
Instruments
1850
The Quebec City Observatory is established on the Plains of Abraham.
Observatories
1854
William Frederick King is born.
Astronomers
1856
The Kingston Observatory is established in London, Ontario.
Observatories
1859
German chemist Robert Wilhelm Bunsen and German physicist Gustav Robert Kirchhoff invent the first spectroscope.
Instruments
1863
The McGill University Observatory is established in Montreal, Quebec.
Observatories
1873
The Charles Blackman Observatory is established in Montreal, Quebec.
Observatories
1879
American inventor George Eastman (who would go on to found the Eastman-Kodak company in 1892) builds a machine for coating photographic plates with emulsion, which allows for the mass production of photographs.
Instruments
1879
The Woodstock College Observatory is established in Hamilton, Ontario.
Observatories
1879
Edison makes a major improvement on the electric light bulb.
Observatories
1882
The Victoria College Observatory is established in Cobourg, Ontario.
Observatories
1891
American physicist Albert Abraham Michelson constructs the first interferometer.
Instruments

1992
UNESCO dedicates a special section to the conservation of the sky and its purity in its "Declaration of the rights for future generations".
Observatories
2002
More than 95% of stars are no longer visible from large Canadian cities. About two thirds of Canadians can no longer see the Milky Way.
Observatories